This blog is intended to provide an overview of Flutter architecture and how it executes Dart code behind the scenes on the mobile devices. The language used in this blog is very simplistic so that any mobile developer learning Flutter can understand how it works underneath.
Flutter Architecture
The Flutter architecture has three layers. Each layer comprises of bunch of libraries. Let’s look at these layers in detail.
- Framework
- Engine
- Embedder
Framework
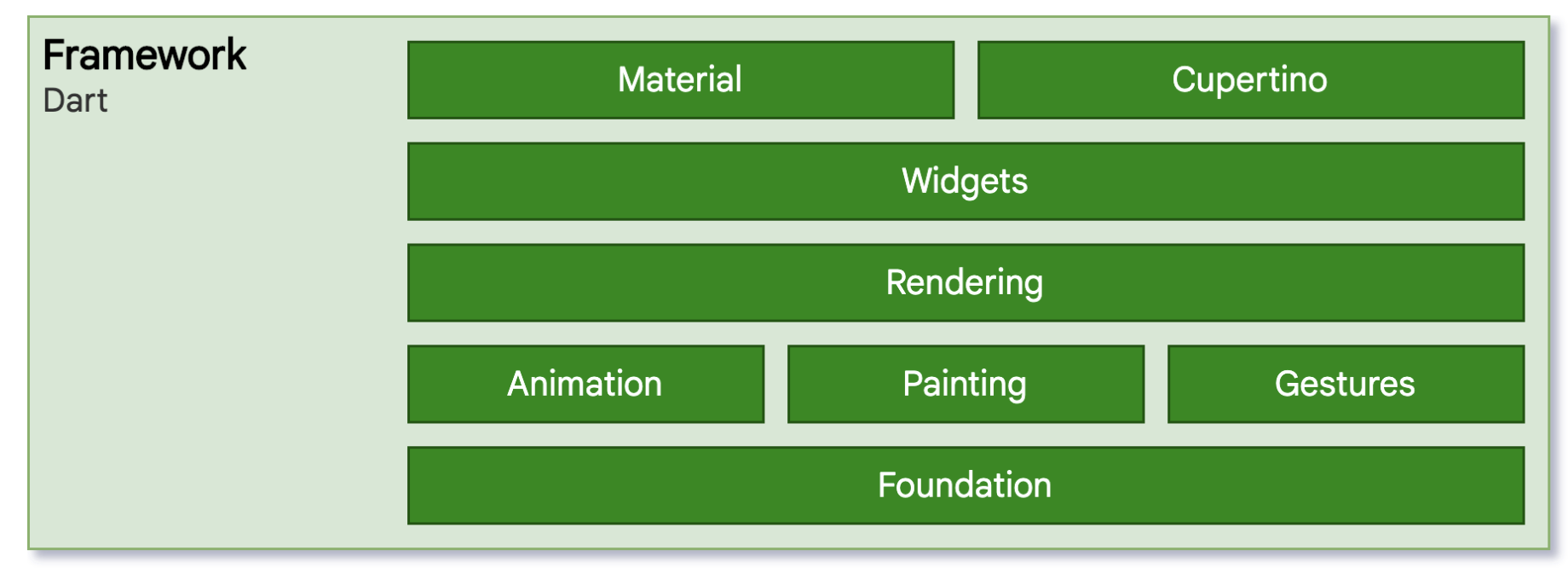
Developers interact with Flutter using the framework layer. It holds multiple components using which devs write the application logic. At a high level it contains widgets, animations, rendering logic etc. It also provides the Material & Cupertino libraries which helps in implementing the Material and iOS designs.
Components
- Foundation: These are basic foundation classes which provides basic building blocks like animation, painting, gestures etc.
- Rendering: This layer is an abstraction over layout. It helps in building a tree of renderable objects. It also figures out the dirty objects in the widget tree and replace them with new ones. Similar to what React Native provides with virtual DOM.
- Widgets: It provides all the widgets required to compose the layout. Each UI component in flutter has a corresponding widget class.
- Material & Cupertino: These libraries convert layout designed using widgets into Material or iOS designs.
Apart from above components Flutter Framework also provides many high-level features that developers need to build apps such as Http, Animations, In app payments etc.
Engine
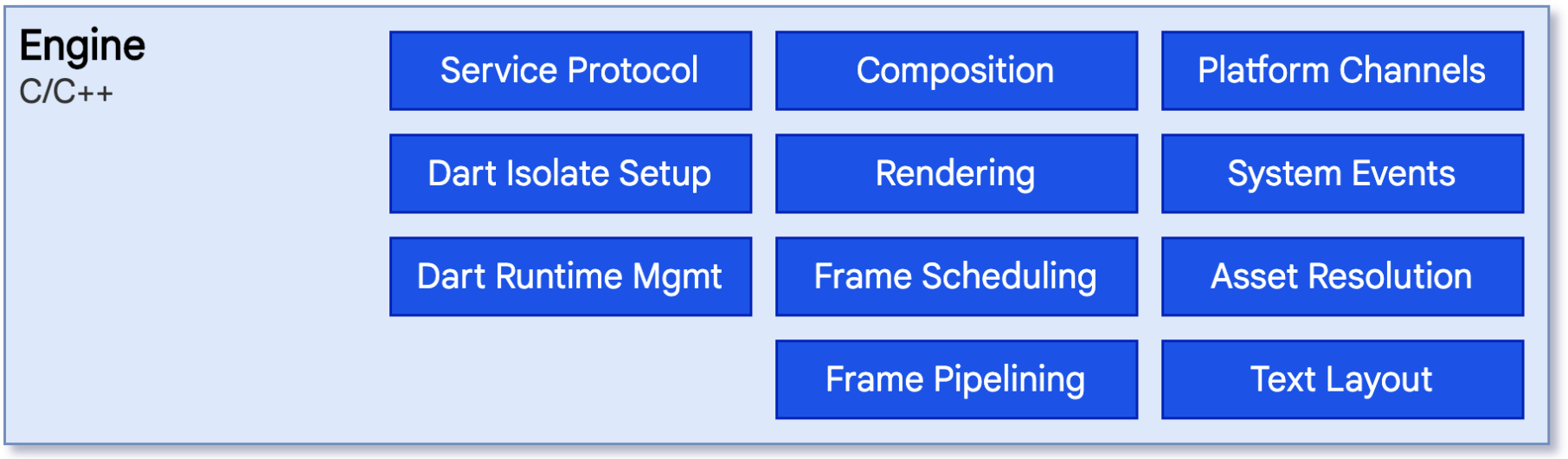
Flutter Engine is written in C/C++. The engine provides low level implementation of Flutter’s core APIs including graphics, text layout, file and network I/O, accessibility support, plugin architecture, and a Dart runtime. Engine is responsible for running the compiled dart code with the help of dart runtime on the device.
Embedder
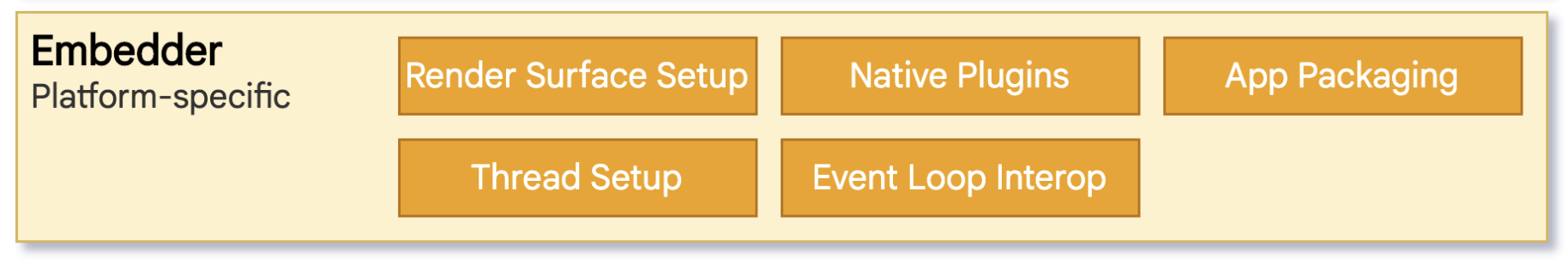
Flutter Embedder provides the entrypoint for the Flutter app. It intializes the Flutter Engine and obtains threads for UI. Embedder also manages the app lifecycle and responsible for input gestures such as mouse, keyboard and touch. Embedder code is platform specific and written in the native platform’s language. For example Android’s Embedder is written in Java/C++ and iOS Embeder is in Objective-C/Objective-C++.
How Flutter code runs on device
Below is a simplistic representation of how the dart code runs on device.
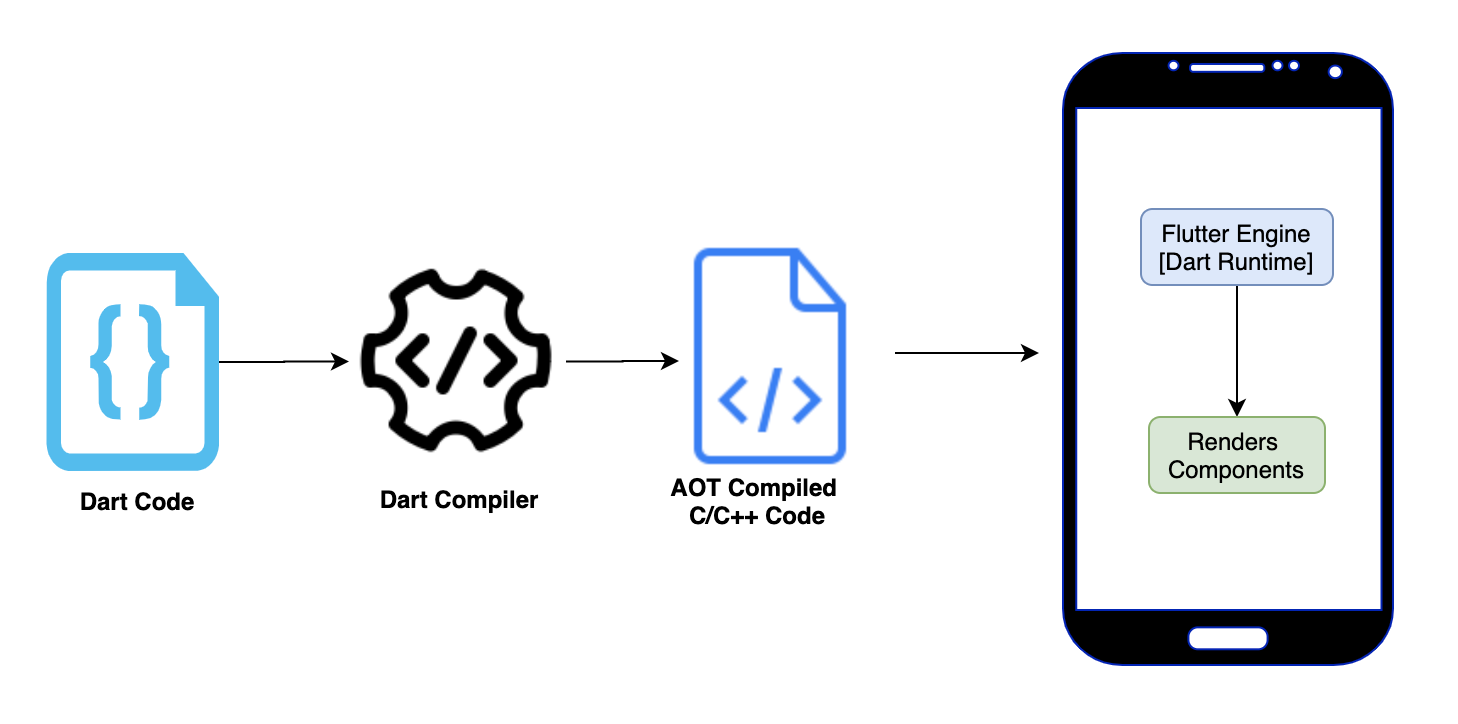
Steps:
- First of all the Dart code is compiled into AOT (Ahead of time) native, ARM library code.
- The compiled native code is embedded into apk or ipa file
- When user opens the app, Flutter Embedder code kicks in
- Flutter Embedder intializes the Flutter app
- Dart runtime takes the native code and starts executing it
Want to learn more about flutter? Flutter has a very detailed documentation which is available on Flutter’s website.