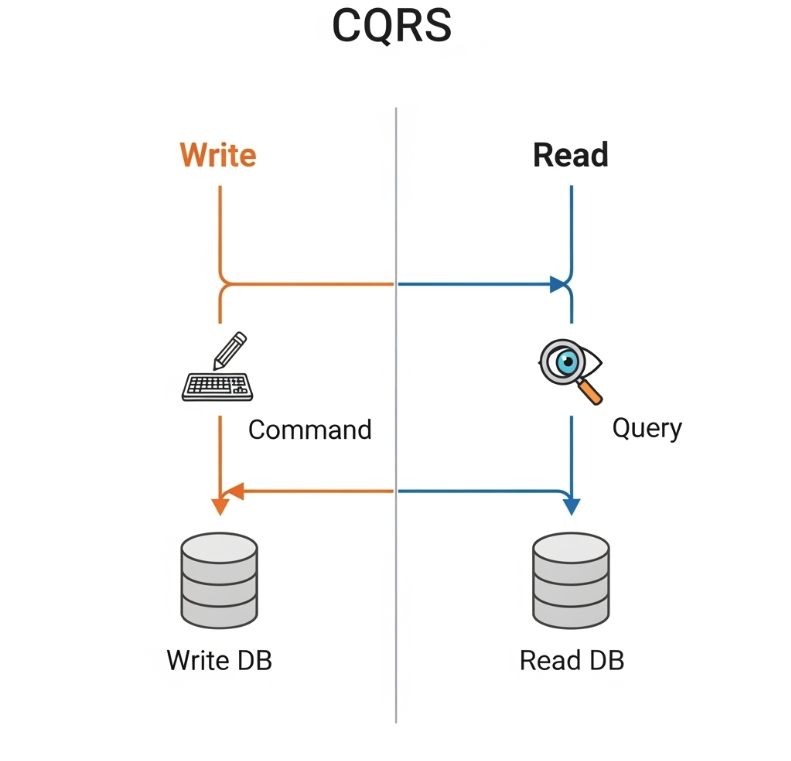
What is a Service Mesh?
A service mesh is a layer that sits between your microservices and handles all the communication between them. Instead of each service managing its own retries, timeouts, security, and monitoring, the mesh does it for you. Think of it like a smart network that knows how to route traffic, handle failures, and keep things secure automatically.
Think of it like: A traffic control system for your services. Every message goes through the mesh, which makes sure it gets to the right place safely and efficiently.
The Problem: Service Communication Gets Messy
Without Service Mesh
Each service handles its own communication:
Every service needs:
• Retry logic for failed calls
• Security and encryption code
• Load balancing logic
• Monitoring and metrics
• Circuit breaker patterns
Same code repeated everywhere!
Problem: Lots of duplicate code. Hard to update. Easy to make mistakes.
With Service Mesh
Mesh handles all communication concerns:
Services just make calls
↓
Mesh intercepts all traffic
↓
Automatically handles:
✓ Retries and timeouts
✓ Security and encryption
✓ Load balancing
✓ Monitoring everything
Result: Services stay simple. Changes happen in one place. Consistent behavior everywhere.
How Service Mesh Works
graph TB
M[Control Plane]
M -.->|manage| P1
M -.->|manage| P2
subgraph Service A
A1[App A] --> P1[Proxy]
end
subgraph Service B
P2[Proxy] --> B1[App B]
end
P1 <-->|encrypted| P2
style A1 fill:#e0f2fe,stroke:#0369a1,stroke-width:2px
style B1 fill:#e0f2fe,stroke:#0369a1,stroke-width:2px
style P1 fill:#dcfce7,stroke:#16a34a,stroke-width:2px
style P2 fill:#dcfce7,stroke:#16a34a,stroke-width:2px
style M fill:#fef3c7,stroke:#f59e0b,stroke-width:2px
Each service gets a proxy (called a "sidecar") that handles all network traffic. The control plane manages all proxies from one central place.
Key Features
- Traffic Management: Route traffic between services, split requests for testing, and handle retries automatically.
- Security: Automatically encrypt all service-to-service traffic and control which services can talk to each other.
- Observability: See all traffic flowing between services, track response times, and find bottlenecks.
- Reliability: Automatic retries when things fail, circuit breakers to stop calling broken services, and timeouts.
Traffic Flow with Service Mesh
sequenceDiagram
participant UserService
participant ProxyA as Proxy (Sidecar)
participant ProxyB as Proxy (Sidecar)
participant OrderService
Note over UserService,OrderService: User service calls order service
UserService->>ProxyA: Make request
Note over ProxyA: Add encryption, Add headers, Apply retry logic
ProxyA->>ProxyB: Encrypted request
Note over ProxyB: Decrypt, Check auth, Record metrics
ProxyB->>OrderService: Forward request
OrderService-->>ProxyB: Response
ProxyB-->>ProxyA: Encrypted response
ProxyA-->>UserService: Response
Note over UserService,OrderService: All traffic secured and monitored automatically
Popular Service Meshes
- Istio: Most popular and feature-rich. Works with Kubernetes. Powerful but can be complex to set up and manage.
- Linkerd: Lightweight and simple to use. Built specifically for Kubernetes. Great for getting started with service mesh.
- Consul Connect: Part of HashiCorp Consul. Works across different platforms, not just Kubernetes. Good if you need multi-cloud.
- AWS App Mesh: AWS managed service mesh. Integrates well with other AWS services. Easy if you're already on AWS.
When to Use Service Mesh
Use Service Mesh When
- You have many microservices
- Services need secure communication
- You want better observability
- Need traffic splitting for deployments
- Want consistent retry and timeout logic
- Running on Kubernetes
Skip Service Mesh When
- You have just a few services (3-5)
- Simple architecture is enough
- Team is small and new to ops
- Limited resources for management
- Services rarely talk to each other
- Performance overhead is critical