What is CQRS?
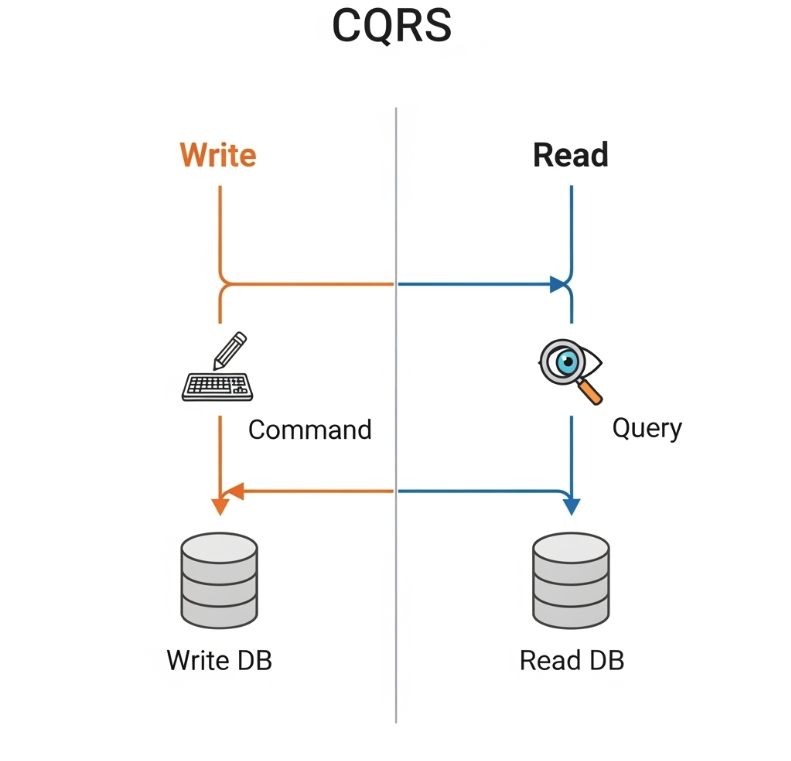
Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) is an architectural pattern that separates read and write operations for data stores. Instead of using one model for both reading and writing data, CQRS uses separate models for each operation.
Command Side
Handles writes, updates, and deletes
• Focused on business logic
• Validates and processes commands
• Optimized for write operations
• Maintains data consistency
• Validates and processes commands
• Optimized for write operations
• Maintains data consistency
Query Side
Handles reads and data retrieval
• Optimized for fast queries
• No business logic
• Can use different data models
• Supports multiple view formats
• No business logic
• Can use different data models
• Supports multiple view formats
System Architecture Flow
graph TD
A[User Request] --> B{Router}
B -->|Command| C[Command Handler]
B -->|Query| D[Query Handler]
C --> E[Write DB]
D --> F[Read DB]
E -.->|Sync| F
style A fill:#f1f5f9,stroke:#64748b,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#faf5f0,stroke:#92400e,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#f0f9f0,stroke:#365314,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#f0f9f0,stroke:#365314,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#f5f3ff,stroke:#7c3aed,stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#f5f3ff,stroke:#7c3aed,stroke-width:2px
Key Benefits
- Performance: Read and write operations can be optimized independently for their specific use cases
- Scalability: Scale read and write databases separately based on actual usage patterns
- Security: Different security models for read vs write operations
- Flexibility: Use different data models and storage technologies for reads vs writes
When to Use CQRS
Good For:
- High-read, low-write applications
- Complex business logic on write operations
- Need different data models for reads vs writes
- Performance-critical read operations
- Collaborative domains with many concurrent users
- Event-driven architectures
Avoid When:
- Simple CRUD applications
- Strong consistency requirements
- Small development team
- Tight coupling between read and write operations
- Real-time data requirements
- Limited infrastructure resources
Event Sourcing Integration
CQRS pairs perfectly with Event Sourcing to create a complete audit trail and enable powerful replay capabilities.
Commands
Generate events instead of directly updating state
Event Store
Stores all events as the source of truth
Projections
Build read models from events
Common Challenges
-
Data Consistency: Managing eventual consistency between read and write models can be complex and requires careful design.
Solution: Implement proper event handling, monitoring, and compensating actions for failed operations.
-
Increased Complexity: Additional infrastructure, development overhead, and more moving parts to manage and monitor.
Solution: Start simple, evolve architecture gradually, and invest in good tooling and automation.
-
Debugging Difficulties: Tracing issues across separate read/write systems and asynchronous operations.
Solution: Implement comprehensive logging, distributed tracing, and monitoring tools.
Advertisement